Jede Cloud-to-cloud-Integration muss einen Mechanismus zur Authentifizierung von Nutzern enthalten.
Über die Authentifizierung kannst du die Google-Konten deiner Nutzer mit Nutzerkonten in deinem Authentifizierungssystem verknüpfen. So kannst du Nutzer identifizieren, wenn deine Auftragsausführung einen Smart-Home-Intent empfängt. Google Smart Home unterstützt nur OAuth mit einem Autorisierungscode-Ablauf.
Auf dieser Seite wird beschrieben, wie Sie Ihren OAuth 2.0-Server so einrichten, dass er mit Ihrer Cloud-to-cloud-Integration funktioniert.
Google-Kontoverknüpfung mit OAuth
Beim Autorisierungscode-Ablauf sind zwei Endpunkte erforderlich:
Der Autorisierungsendpunkt, über den die Anmeldeoberfläche für Nutzer angezeigt wird, die noch nicht angemeldet sind. Am Autorisierungsendpunkt wird auch ein kurzlebiger Autorisierungscode erstellt, um die Einwilligung der Nutzer für den angeforderten Zugriff aufzuzeichnen.
Der Tokenaustausch-Endpunkt, der für zwei Arten von Austauschvorgängen zuständig ist:
- Tauscht einen Autorisierungscode gegen ein langlebiges Aktualisierungstoken und ein kurzlebiges Zugriffstoken ein. Dieser Austausch findet statt, wenn der Nutzer den Ablauf zur Kontoverknüpfung durchläuft.
- Tauscht ein langlebiges Aktualisierungstoken gegen ein kurzlebiges Zugriffstoken ein. Dieser Austausch erfolgt, wenn Google ein neues Zugriffstoken benötigt, weil das vorhandene abgelaufen ist.
Gestaltungsrichtlinien
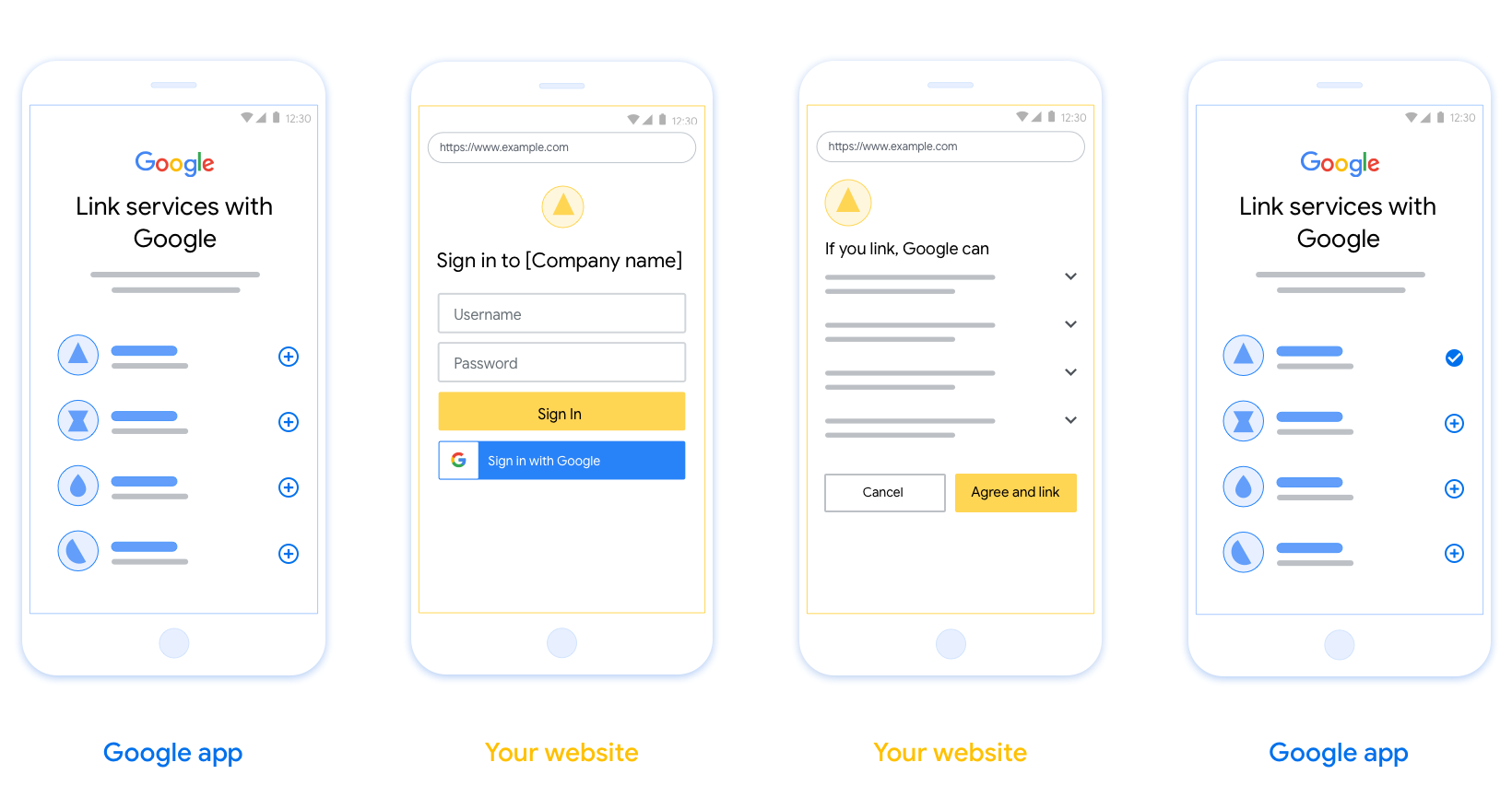
In diesem Abschnitt werden die Designanforderungen und ‑empfehlungen für den Nutzerbildschirm beschrieben, den Sie für OAuth-Verknüpfungsabläufe hosten. Nachdem die Funktion von der Google-App aufgerufen wurde, zeigt Ihre Plattform dem Nutzer eine Anmeldeseite für Google und einen Bildschirm für die Einwilligung zur Kontoverknüpfung an. Nachdem der Nutzer der Kontoverknüpfung zugestimmt hat, wird er zur Google-App zurückgeleitet.
Voraussetzungen
- Sie müssen dem Nutzer mitteilen, dass sein Konto mit Google verknüpft wird, nicht mit einem bestimmten Google-Produkt wie Google Home oder Google Assistant.
- Du musst über eine Google-Autorisierungserklärung verfügen, z. B. „Durch die Anmeldung autorisierst du Google, deine Geräte zu steuern.“ Weitere Informationen finden Sie im Abschnitt Autorisierung für die Gerätesteuerung durch Google der Google Home-Entwicklerrichtlinien.
- Sie müssen die Web-OAuth-Verknüpfungsseite öffnen und dafür sorgen, dass Nutzer sich auf einfache Weise in ihrem Google-Konto anmelden können, z. B. über Felder für ihren Nutzernamen und ihr Passwort. Verwenden Sie nicht die Google-Anmeldemethode (GSI), mit der Nutzer verknüpfen können, ohne zur Web-OAuth-Verknüpfungsseite weitergeleitet zu werden. Es stellt einen Verstoß gegen die Google-Richtlinien dar.
- Sie müssen mindestens eines der folgenden Elemente auf der OAuth-Verknüpfungsseite angeben, um die Integration anzugeben, mit der der Nutzer eine Verknüpfung herstellt:
- Firmenlogo
- Name des Unternehmens
- Name der Integration
- App-Symbol
Empfehlungen
Wir empfehlen Folgendes:
Datenschutzerklärung von Google anzeigen Fügen Sie auf dem Zustimmungsbildschirm einen Link zur Datenschutzerklärung von Google ein.
Zu teilende Daten: Verwenden Sie eine klare und prägnante Sprache, um dem Nutzer mitzuteilen, welche seiner Daten Google benötigt und warum.
Klarer Call-to-Action: Geben Sie auf dem Einwilligungsbildschirm einen klaren Call-to-Action an, z. B. „Zustimmen und verknüpfen“. Nutzer müssen wissen, welche Daten sie mit Google teilen müssen, um ihre Konten zu verknüpfen.
Möglichkeit zur Kündigung Bieten Sie Nutzern die Möglichkeit, zurückzugehen oder abzubrechen, wenn sie keine Verknüpfung herstellen möchten.
Übersichtlicher Anmeldevorgang: Sorgen Sie dafür, dass Nutzer sich auf einfache Weise in ihrem Google-Konto anmelden können, z. B. über Felder für ihren Nutzernamen und ihr Passwort oder über Mit Google anmelden.
Verknüpfung aufheben: Bieten Sie Nutzern eine Möglichkeit, die Verknüpfung aufzuheben, z. B. eine URL zu ihren Kontoeinstellungen auf Ihrer Plattform. Alternativ können Sie einen Link zu Google-Konto einfügen, über den Nutzer ihr verknüpftes Konto verwalten können.
Nutzerkonto ändern: Schlagen Sie Nutzern eine Methode vor, mit der sie ihr(e) Konto(s) wechseln können. Das ist besonders dann von Vorteil, wenn Nutzer mehrere Konten haben.
- Wenn ein Nutzer den Zustimmungsbildschirm schließen muss, um das Konto zu wechseln, senden Sie einen behebaren Fehler an Google, damit sich der Nutzer mit OAuth-Verknüpfung im gewünschten Konto anmelden kann.
Fügen Sie Ihr Logo ein. Ihr Unternehmenslogo auf dem Zustimmungsbildschirm anzeigen Platzieren Sie Ihr Logo gemäß Ihren Style-Richtlinien. Wenn Sie auch das Google-Logo anzeigen möchten, lesen Sie den Abschnitt Logos und Marken.
Autorisierungscode-Ablauf
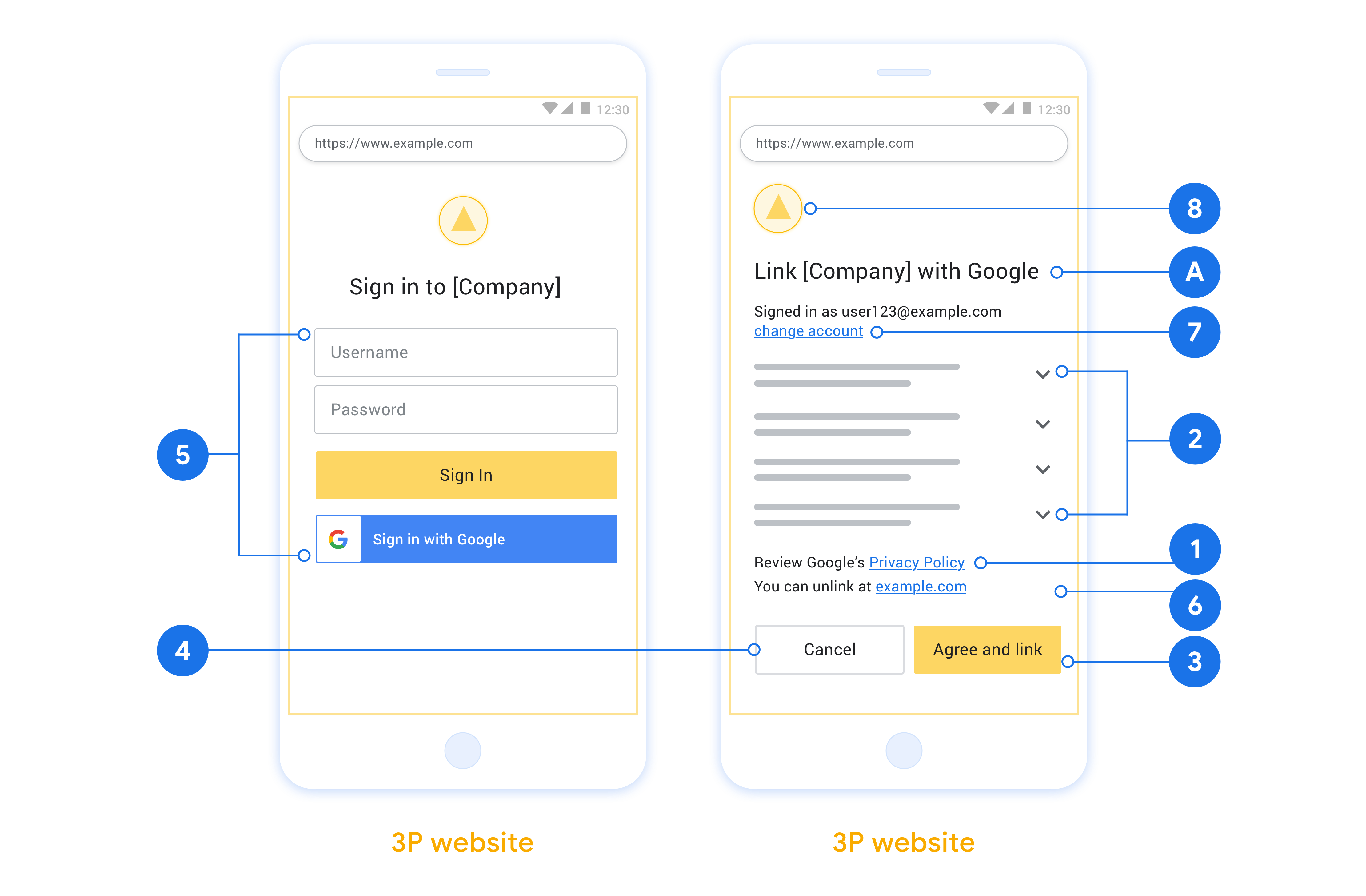
Eine OAuth 2.0-Serverimplementierung des Autorisierungscode-Vorgangs besteht aus zwei Endpunkten, die Ihr Dienst über HTTPS zur Verfügung stellt. Der erste Endpunkt ist der Autorisierungsendpunkt, der dafür zuständig ist, die Einwilligung von Nutzern für den Datenzugriff zu finden oder einzuholen. Der Autorisierungsendpunkt präsentiert Ihren Nutzern, die noch nicht angemeldet sind, eine Anmelde-UI und zeichnet die Einwilligung in den angeforderten Zugriff auf. Der zweite Endpunkt ist der Token-Austausch-Endpunkt, der verwendet wird, um verschlüsselte Strings (Tokens) zu erhalten, die einen Nutzer zum Zugriff auf Ihren Dienst autorisieren.
Wenn eine Google-Anwendung eine der APIs Ihres Dienstes aufrufen muss, verwendet Google diese Endpunkte, um die Erlaubnis Ihrer Nutzer einzuholen, diese APIs in ihrem Namen aufzurufen.
Eine von Google initiierte OAuth 2.0-Sitzung mit Autorisierungscode läuft so ab:
- Google öffnet Ihren Autorisierungsendpunkt im Browser des Nutzers. Wenn der Ablauf für eine Aktion auf einem Gerät ohne Display gestartet wurde, überträgt Google die Ausführung auf ein Smartphone.
- Der Nutzer meldet sich an, sofern er noch nicht angemeldet ist, und erteilt Google die Berechtigung, mit Ihrer API auf seine Daten zuzugreifen, sofern er die Berechtigung noch nicht erteilt hat.
- Ihr Dienst erstellt einen Autorisierungscode und gibt ihn an Google zurück. Leiten Sie dazu den Browser des Nutzers mit dem Autorisierungscode, der an die Anfrage angehängt ist, zurück zu Google weiter.
- Google sendet den Autorisierungscode an Ihren Token-Austausch-Endpunkt, der die Authentizität des Codes prüft und ein Zugriffstoken und ein Aktualisierungstoken zurückgibt. Das Zugriffstoken ist ein kurzlebiges Token, das Ihr Dienst als Anmeldedaten für den Zugriff auf APIs akzeptiert. Das Aktualisierungstoken ist ein Token mit langer Gültigkeitsdauer, das Google speichern und verwenden kann, um neue Zugriffstokens abzurufen, wenn diese ablaufen.
- Nachdem der Nutzer den Vorgang für die Kontoverknüpfung abgeschlossen hat, enthält jede nachfolgende Anfrage von Google ein Zugriffstoken.
Autorisierungsanfragen verarbeiten
Wenn Sie die Kontoverknüpfung mit dem OAuth 2.0-Autorisierungscode-Flow durchführen müssen, leitet Google den Nutzer mit einer Anfrage, die die folgenden Parameter enthält, an Ihren Autorisierungsendpunkt weiter:
| Parameter des Autorisierungsendpunkts | |
|---|---|
client_id |
Die Client-ID, die Sie Google zugewiesen haben. |
redirect_uri |
Die URL, an die Sie die Antwort auf diese Anfrage senden. |
state |
Nachverfolgungswert, der unverändert in der Weiterleitungs-URI an Google zurückgegeben wird. |
scope |
Optional:Eine durch Leerzeichen getrennte Gruppe von Bereichs-Strings, die die Daten angibt, für die Google eine Autorisierung anfordert. |
response_type |
Der Typ des Werts, der in der Antwort zurückgegeben werden soll. Im OAuth 2.0-Vorgang mit Autorisierungscode ist der Antworttyp immer code.
|
Wenn Ihr Autorisierungsendpunkt beispielsweise unter https://myservice.example.com/auth verfügbar ist, könnte eine Anfrage so aussehen:
GET https://myservice.example.com/auth?client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&state=STATE_STRING&scope=REQUESTED_SCOPES&response_type=code
Damit Ihr Autorisierungsendpunkt Anmeldeanfragen verarbeiten kann, führen Sie die folgenden Schritte aus:
- Prüfen Sie, ob
client_idmit der Client-ID übereinstimmt, die Sie Google zugewiesen haben, und obredirect_urimit der von Google für Ihren Dienst bereitgestellten Weiterleitungs-URL übereinstimmt. Diese Prüfungen sind wichtig, um zu verhindern, dass unbeabsichtigten oder falsch konfigurierten Client-Apps Zugriff gewährt wird. Wenn Sie mehrere OAuth 2.0-Abläufe unterstützen, prüfen Sie auch, obresponse_typecodeist. - Prüfen Sie, ob der Nutzer in Ihrem Dienst angemeldet ist. Wenn der Nutzer nicht angemeldet ist, schließen Sie den Anmelde- oder Registrierungsvorgang Ihres Dienstes ab.
- Autorisierungscode für Google generieren, damit Google auf Ihre API zugreifen kann. Der Autorisierungscode kann ein beliebiger Stringwert sein, muss aber den Nutzer, den Client, für den das Token bestimmt ist, und die Ablaufzeit des Codes eindeutig repräsentieren und darf nicht erraten werden können. Normalerweise geben Sie Autorisierungscodes aus, die nach etwa 10 Minuten ablaufen.
- Prüfen Sie, ob die URL, die durch den Parameter
redirect_uriangegeben wird, folgendes Format hat:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID https://oauth-redirect-sandbox.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID
- Leiten Sie den Browser des Nutzers zur URL weiter, die durch den Parameter
redirect_uriangegeben wird. Fügen Sie den Autorisierungscode, den Sie gerade generiert haben, und den ursprünglichen, unveränderten Statuswert ein, wenn Sie die Weiterleitung vornehmen, indem Sie die Parametercodeundstateanhängen. Das ist ein Beispiel für die resultierende URL:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID?code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&state=STATE_STRING
Tokenaustauschanfragen verarbeiten
Der Token-Austauschendpunkt Ihres Dienstes ist für zwei Arten von Token-Austauschvorgängen zuständig:
- Autorisierungscodes gegen Zugriffstokens und Aktualisierungstokens eintauschen
- Aktualisierungstokens gegen Zugriffstokens tauschen
Tokenaustauschanfragen enthalten die folgenden Parameter:
| Parameter für den Token-Exchange-Endpunkt | |
|---|---|
client_id |
Ein String, der Google als Ursprung der Anfrage identifiziert. Dieser String muss in Ihrem System als eindeutige Kennung von Google registriert sein. |
client_secret |
Ein geheimer String, den Sie bei Google für Ihren Dienst registriert haben. |
grant_type |
Der Typ des Tokens, der ausgetauscht wird. Es ist entweder authorization_code oder refresh_token. |
code |
Wenn grant_type=authorization_code, ist dieser Parameter der Code, den Google von Ihrem Anmelde- oder Tokenaustausch-Endpunkt erhalten hat. |
redirect_uri |
Wenn grant_type=authorization_code, ist dieser Parameter die URL, die in der ursprünglichen Autorisierungsanfrage verwendet wird. |
refresh_token |
Wenn grant_type=refresh_token, ist dieser Parameter das Aktualisierungstoken, das Google von Ihrem Token-Austausch-Endpunkt erhalten hat. |
Konfigurieren, wie Google Anmeldedaten an Ihren Server sendet
Je nach Implementierung erwartet Ihr Autorisierungsserver, dass er Clientanmeldedaten entweder im Anfragetext oder im Anfrageheader empfängt.
Standardmäßig sendet Google die Anmeldedaten im Anfragetext. Wenn Ihr Autorisierungsserver erfordert, dass sich die Clientanmeldedaten im Anfrageheader befinden, müssen Sie Ihre Cloud-to-cloud-Integration entsprechend konfigurieren:
Klicken Sie in der Projektliste neben dem Projekt, das Sie bearbeiten möchten, auf Öffnen.
Wählen Sie unter Cloud-to-Cloud die Option Entwickeln aus.
Klicken Sie neben Ihrer Integration auf Öffnen.
Scrollen Sie nach unten zum Abschnitt Berechtigungen (optional) und klicken Sie das Kästchen Zulassen, dass Google die Client-ID und den Clientschlüssel über den Header für die HTTP-Basic-Authentifizierung überträgt an.
Klicken Sie auf Save (Speichern), um Ihre Änderungen zu übernehmen.
Autorisierungscodes gegen Zugriffstokens und Aktualisierungstokens eintauschen
Nachdem sich der Nutzer angemeldet hat und Ihr Autorisierungs-Endpunkt einen kurzlebigen Autorisierungscode an Google zurückgegeben hat, sendet Google eine Anfrage an Ihren Token-Austausch-Endpunkt, um den Autorisierungscode gegen ein Zugriffstoken und ein Aktualisierungstoken einzutauschen.
Bei diesen Anfragen ist der Wert von grant_type authorization_code und der Wert von code der Wert des Autorisierungscodes, den Sie Google zuvor gewährt haben. Im Folgenden sehen Sie ein Beispiel für eine Anfrage zum Tauschen eines Autorisierungscodes gegen ein Zugriffstoken und ein Aktualisierungstoken:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=authorization_code&code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI
Wenn Sie Autorisierungscodes gegen ein Zugriffstoken und ein Aktualisierungstoken eintauschen möchten, antwortet Ihr Endpunkt für den Tokenaustausch auf POST-Anfragen, indem er die folgenden Schritte ausführt:
- Prüfen Sie, ob
client_idden Ursprung der Anfrage als autorisierten Ursprung identifiziert und obclient_secretmit dem erwarteten Wert übereinstimmt. - Prüfen Sie, ob der Autorisierungscode gültig und nicht abgelaufen ist und ob die in der Anfrage angegebene Client-ID mit der Client-ID übereinstimmt, die dem Autorisierungscode zugeordnet ist.
- Prüfen Sie, ob die im Parameter
redirect_uriangegebene URL mit dem Wert übereinstimmt, der in der ursprünglichen Autorisierungsanfrage verwendet wurde. - Wenn Sie nicht alle oben genannten Kriterien bestätigen können, geben Sie den HTTP-Fehler 400 Bad Request mit
{"error": "invalid_grant"}als Text zurück. - Verwenden Sie andernfalls die Nutzer-ID aus dem Autorisierungscode, um ein Aktualisierungstoken und ein Zugriffstoken zu generieren. Diese Tokens können einen beliebigen Stringwert haben, müssen aber den Nutzer und den Client, für den das Token bestimmt ist, eindeutig repräsentieren und dürfen nicht erraten werden können. Erfassen Sie für Zugriffstokens auch die Ablaufzeit des Tokens, die in der Regel eine Stunde nach der Ausstellung des Tokens liegt. Aktualisierungstokens laufen nicht ab.
- Geben Sie das folgende JSON-Objekt im Text der HTTPS-Antwort zurück:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Google speichert das Zugriffstoken und das Aktualisierungstoken für den Nutzer und zeichnet den Ablauf des Zugriffstokens auf. Wenn das Zugriffstoken abläuft, verwendet Google das Aktualisierungstoken, um ein neues Zugriffstoken von Ihrem Token-Austausch-Endpunkt abzurufen.
Aktualisierungstokens gegen Zugriffstokens tauschen
Wenn ein Zugriffstoken abläuft, sendet Google eine Anfrage an Ihren Token-Austauschendpunkt, um ein Aktualisierungstoken gegen ein neues Zugriffstoken einzutauschen.
Bei diesen Anfragen ist der Wert von grant_type gleich refresh_token und der Wert von refresh_token ist der Wert des Aktualisierungstokens, das Sie Google zuvor gewährt haben. Das folgende Beispiel zeigt eine Anfrage zum Austausch eines Aktualisierungstokens gegen ein Zugriffstoken:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN
Wenn Sie ein Aktualisierungstoken gegen ein Zugriffstoken eintauschen möchten, führt Ihr Token-Austausch-Endpunkt die folgenden Schritte aus, wenn er auf POST-Anfragen reagiert:
- Prüfen Sie, ob
client_idGoogle als Ursprung der Anfrage identifiziert und obclient_secretmit dem erwarteten Wert übereinstimmt. - Prüfen Sie, ob das Aktualisierungstoken gültig ist und ob die in der Anfrage angegebene Client-ID mit der Client-ID übereinstimmt, die dem Aktualisierungstoken zugeordnet ist.
- Wenn Sie nicht alle oben genannten Kriterien bestätigen können, geben Sie den HTTP-Fehler 400 (Ungültige Anfrage) mit
{"error": "invalid_grant"}als Text zurück. - Andernfalls verwenden Sie die Nutzer-ID aus dem Aktualisierungstoken, um ein Zugriffstoken zu generieren. Diese Tokens können beliebige String-Werte sein, müssen aber den Nutzer und den Client, für den das Token bestimmt ist, eindeutig repräsentieren und dürfen nicht erraten werden können. Notieren Sie für Zugriffstokens auch die Ablaufzeit des Tokens, in der Regel eine Stunde nach der Ausstellung des Tokens.
- Geben Sie das folgende JSON-Objekt im Text der HTTPS-Antwort zurück:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
userinfo-Anfragen verarbeiten
Der userinfo-Endpunkt ist eine geschützte OAuth 2.0-Ressource, die Ansprüche über den verknüpften Nutzer zurückgibt. Die Implementierung und das Hosten des userinfo-Endpunkts sind mit Ausnahme der folgenden Anwendungsfälle optional:
- Anmeldung in einem verknüpften Konto über Google One Tap.
- Reibungsloses Abo auf Android TV
Nachdem das Zugriffstoken erfolgreich von Ihrem Tokenendpunkt abgerufen wurde, sendet Google eine Anfrage an Ihren userinfo-Endpunkt, um grundlegende Profilinformationen über den verknüpften Nutzer abzurufen.
| Anfrageheader für userinfo-Endpunkt | |
|---|---|
Authorization header |
Das Zugriffstoken vom Typ „Bearer“. |
Wenn Ihr userinfo-Endpunkt beispielsweise unter
https://myservice.example.com/userinfo, kann eine Anfrage so aussehen:
GET /userinfo HTTP/1.1 Host: myservice.example.com Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN
Führen Sie die folgenden Schritte aus, damit der userinfo-Endpunkt Anfragen verarbeiten kann:
- Extrahieren Sie das Zugriffstoken aus dem Autorisierungs-Header und geben Sie Informationen für den Nutzer zurück, der mit dem Zugriffstoken verknüpft ist.
- Wenn das Zugriffstoken ungültig ist, gib den Fehler „HTTP 401 Unauthorized“ mit dem Antwortheader
WWW-Authenticatezurück. Hier ist ein Beispiel für eine Userinfo-Fehlerantwort:HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized WWW-Authenticate: error="invalid_token", error_description="The Access Token expired"
Wenn das Zugriffstoken gültig ist, geben Sie eine HTTP 200-Antwort mit dem folgenden JSON-Objekt im Text des HTTPS-Objekts zurück. Antwort:
{ "sub": "USER_UUID", "email": "EMAIL_ADDRESS", "given_name": "FIRST_NAME", "family_name": "LAST_NAME", "name": "FULL_NAME", "picture": "PROFILE_PICTURE", }Userinfo-Endpunktantwort subEine eindeutige ID, die den Nutzer in Ihrem System identifiziert. emailE-Mail-Adresse des Nutzers given_nameOptional:Vorname des Nutzers. family_nameOptional:Nachname des Nutzers. nameOptional:Vollständiger Name des Nutzers. pictureOptional:Profilbild des Nutzers.

