Commissioning in Matter refers to the process of assigning Fabric credentials to a new device. The Commissioner is the device that does the Commissioning process. The Commissionee is the new device that needs to be provisioned into the Fabric.
At a high-level, the commissioning flow can be broken down into multiple stages:
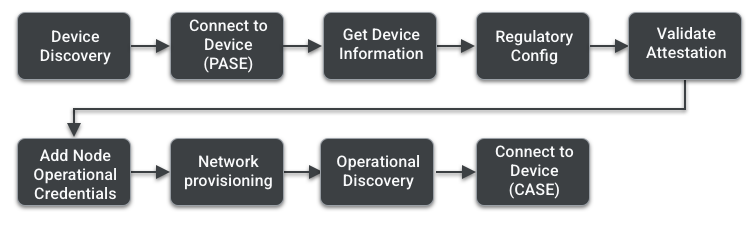
Device discovery
Prior to start of the Commissioning flow, the Commissionee must start advertising itself. The Commissionee may advertise itself using any of the three Commissionable Discovery methods. The Commissionee must also provide the onboarding payload.
Connect to device (PASE)
Once the Commissioner has seen the advertisement and matches up the Discriminator, the Commissioner uses the passcode from the onboarding payload to do Passcode Authenticated Session Establishment (PASE) to connect to the device. This is the method to securely establish keys that both devices will be able to use to establish communication. At this step, the Commissioner also arms a fail-safe. A fail-safe provides a way to roll back the device to its original state if commissioning doesn't complete successfully.
Get Commissionee information
The Commissioner reads all the descriptors from the Commissionee. The
DescriptorCluster is on endpoint 0 of the device and describes all the other
endpoints. Commissioner also reads the Basic Information Cluster which includes
information like the Vendor ID, Product ID, Product Name and the Serial Number.
At this step, the Commissioner also reads the device type of the Commissionee
which helps drive the UX on the Commissioner side.
Regulatory config
The Commissioner configures regulatory information on the Commissionee using the
SetRegulatoryConfig command. Regulatory information includes information like
configuring the location (indoor/outdoor/both) of the device or setting up the
country code.
Commissionee attestation
The goal of the Commissionee attestation procedure is to determine whether a device has been certified and is a genuine Matter device. Commissioner extracts the Device Attestation Certificate (DAC) and the Product Attestation Intermediate (PAI) certificate from the Commissionee. These certificates contain the Vendor ID, Product ID and Attestation Public Key. Once the certificates are received, the Commissioner does a challenge request that should be signed by the Attestation Private Key and uses that to establish the authenticity of the Commissionee.
Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
The Commissioner sends a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) to the Commissionee. The Commissionee creates a unique operational key pair that will be used in a Certificate Authenticated Session Establishment (CASE) later. The Commissionee returns the resulting CSR information back to the Commissioner.
Add Node Operational Certificate (NOC)
The Commissioner uses the CSR information received from the Commissionee and
passes it to the Administrative Domain Manager (ADM) to generate a trusted
Node Operational Certificate (NOC). The Commissioner installs the Root
Certificate on the Commissionee using the AddTrustedRootCertReq command and
then installs the Node Operational Certificate using the AddNOC command.
Network provisioning
The Commissioner configures the operational network on the Commissionee. This
step is needed for Thread or Wi-Fi devices. This step is
not needed for Ethernet Devices where the device is already connected to the
network. It uses ScanNetworks, AddOrUpdateWifiNetwork and ConnectNetwork
commands.
Operational discovery
Once the newly commissioned node is connected to the network, the Commissioner uses Operational Discovery to find the node on the operational network. Operational discovery is the process by which commissioned nodes are found on the operational network using DNS-SD. If the Commissionee is a Wi-Fi device, it will use mDNS to discover the device.
Operational discovery helps the Commissioner and other Nodes in the network know which IP address and port the Commissionee is using.
CASE session establishment
Once the newly commissioned node has been discovered, a CASE session is established between the Commissioner and the device. This session is initiated by the Commissioner and is responded to by the device. In this step, operational certificates are exchanged and a shared trust is established by validating they're in the same logical fabric.
Commissioning complete
The Commissioner uses CASE to send the
CommissioningComplete command to the newly commissioned device. This is the
last step in the commissioning process. CommissioningComplete also
automatically disarms the fail-safe timer. Once commissioning is successfully
completed, the device operates like any other Node on the operational network.
